Selective Laser Melting (SLM) process is one of the AM processes in which the metal parts are produced by melting the metal powder layer-by-layer. Overheating and heat accumulation in critical regions such as overhang surfaces are the important challenges in the SLM process. The real-time control of the process by monitoring the built chamber was one of the solutions that has been introduced in order to adjustment of melt pool size in the critical regions.
Two projects have been defined on SLM process in Additive Manufacturing Lab:
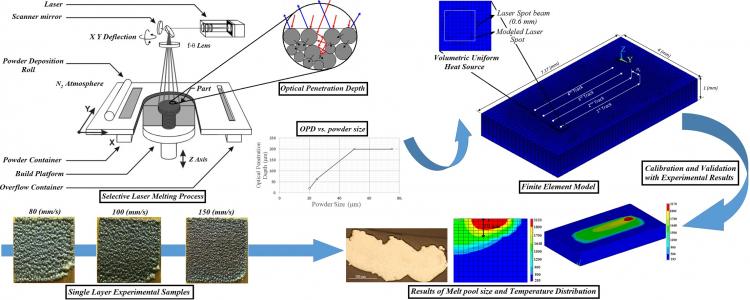
- Finite element simulation of the SLM process: The objectives of one study on this field are, to present a model to propose appropriate amounts of the laser power in critical regions before producing the part, and finite element simulation of the SLM process in order to predict the melt pool size. In this model, the geometry factor is introduced based on the amount of heat sink in each region of the layer. According to the rate of the geometry factor changes in each region, the appropriate amounts of laser power is obtained. The results are as follows:
- The developed Finite Element model is able to predict the melt pool size accurately in the SLM process.
- The rate of change in the width of the melt pool by altering the speed is not the same as that of the depth.
- The melt pool depth of each track stayed almost constant after about 2 mm from the beginning of the track.
- Scanning an overhang layer with constant laser power leads melt pool depth three times larger. While, by using the laser heat input adjustment model, depth of the melt pool increase about 20%.
- The melt pool size in overhang surfaces highly improved by using the laser heat input adjustment model.
|
| Finite Element Simulation of the SLM Process |
This study has been done by Ali Foroozmehr.
2. Experimental study on SLM process: Cellular Lattice Structures (CLS) are a unique classification of materials, which can exhibits a combination of high performance features such as high strength accompanied by a relatively low mass, good energy absorption characteristics and good thermal and acoustic insulation properties. The purpose of fabrication of these structures in the engineering is manufacturing stiff, strong, load- bearing construction using minimum material or where this is useful to be as light as possible. Selective laser melting technology is capable of controlling material distribution everywhere needed, so structures are manufactured in controlled topology and cell shape which affect mechanical properties. The most important interest in the potential of CLS is offered by lightweight metallic construction which is main focus of this research.
Activities:
- Design optimum cell topology with proper strength to weight ratio,
- Modeling and estimating mechanical properties of designed CLS like elastic module and yield stress,
- Producing with SLM technology

|

|
| Cellular Lattice Structures | |
This study is done by Foroozan Forooghi.


